
User Guide for Control Your Crowd (CYC)
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1 Viewing help:
help - 3.2 Check-in a person:
checkin - 3.3 Listing all persons:
listall - 3.4 Listing checked-in persons only:
listcheckedin - 3.5 Finding a person by ID:
find - 3.6 Checkout a person:
checkout - 3.7 Clearing all entries:
clear - 3.8 Edit venue capacity:
editmax - 3.9 Move Storage:
movestorage - 3.10 Exiting the program:
exit - 3.11 Visitor Log
- 3.12 Auto Save
- 3.13 Changing save location
- 3.14 History
- 3.1 Viewing help:
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command summary
1. Introduction
Welcome to the User Guide of Control Your Crowd!
Our application, Control Your Crowd (CYC), will allow you to manage your crowds in real-time. It allows efficient tracking and accessing of visitors’ profiles. You can also easily check-in and check out a visitor, get the current crowd level, limit the venue capacity, save the visitor log for future references, and much more! CYC is an all-in-one application to help event management team, event organizers for events such as Ultra Music Festival manage crowd level with ease. It also works very well for small enterprises and mall management team that needs to monitor influx of visitors.
The application uses a Command Line Interface (CLI); this means that you operate the application by typing commands into a command window. With simple and easy-to-use commands, CYC provides you with efficient crowd management which is faster than traditional Graphical User Interface (GUI) applications can offer. GUI applications allow the user to interact with the application through graphical icons such as buttons and clickable.
Jump to Quick Start to learn how to manage your crowd efficiently with CYC.
2. Quick Start
Prerequisites:
- Ensure that you have Java 11 or above installed in your Computer. If you do not have, you can get it from here.
- Download the latest version of
CYC.jarfrom here. - Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your CYC.
- Open up a command window to the location where your
CYC.jaris located. - Run the command
java -jar CYC.jar [VENUE_MAXIMUM_CAPACITY]. For example,java -jar CYC.jar 500.- Ensure that the
VENUE_MAXIMUM_CAPACITYentered is a positive integer that does not exceed 6 digits.- You can enter input the
VENUE_MAXIMUM_CAPACITYwith or without quotations. For example,500and"500"will both work.
- You can enter input the
- When you are running the
CYC.jaragain, ensure that the[venue maximum capacity]is more than the current number of visitors checked in. Failure to do so will lead to negative maximum venue capacity.
- Ensure that the
-
If the setup is correct, you should see CYC being loaded as shown below (note: your version of CYC would be the latest version).
- Input the command in the command window and press Enter to execute it. Refer to Features for details of each command.
Tips and Additional Notes:
- Maximize the command line window to ensure that you get to make use of the visuals of CYC CLI.
- Do NOT edit the
LogFile.txt,TrackingList.txtorHistory.txtfiles.
- You are only allowed to copy the contents of the
History.txtfile.
3. Features
Notes about the command format:
- Commands are in
lower_case.- Items in square brackets
[ ]are optional.- Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by user.
- E.g. in
checkin n/NAME i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID,NAMEis a parameter that has to be supplied by user. So e.g.checkin n/John i/123A.- Additional parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exit,clear) will be ignored.
- e.g. if the user types
help 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDis unique. (i.e. no two persons will have the same ID)
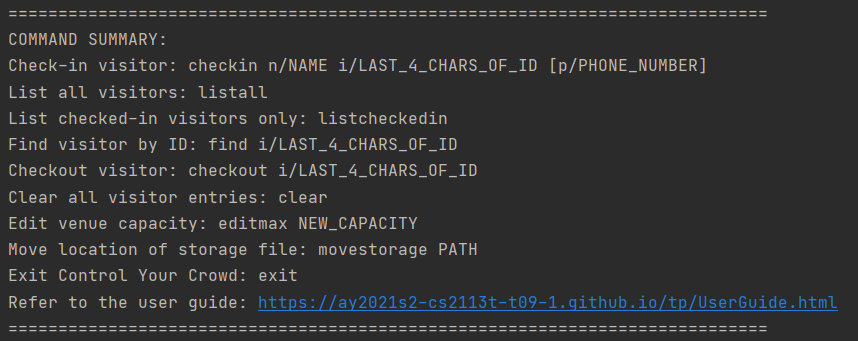
3.1 Viewing help: help
This command will provide you a summary of the all the commands with its corresponding format. This command will help you in situations when you forget the available commands, or their format while on duty.
Format: help
Example Input: help
Example Output:
3.2 Check-in a person: checkin
Supposed there is a visitor,
you can check in a person to CYC via checkin command. After a successful check-in, CYC will also notify you on the
current venue capacity.
Format:
checkin i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID n/NAME [p/PHONE_NUMBER]
- First 3 characters of
LAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDshould be integers. Last character ofLAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDmust be an English alphabet letter. NAMEis optional. If the user has checked in before, entering theLAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDis sufficient to retrieve the user’sNAMEandPHONE_NUMBERfrom previous check in. If the user has not checked in before,NAMEmust be entered.NAMEmust only contain English alphabet letters and empty spaces with a maximum character limit of 30. Any other characters will not be accepted.PHONE_NUMBERis optional.PHONE_NUMBERmust consist of 8 integers, as per local (Singapore) phone number format.
Supposedly John is a new visitor and he wants to check in. Since it is his first time visiting, you should check in John using his
i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID, n/NAME and [p/PHONE_NUMBER] as shown below.
Example Input:
checkin i/123A n/John p/91231112
When John visits again in the future, you would only need to check in
using his i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID as shown below.
checkin i/123A
Example Output:
For both new visitor and returning visitor, you should observe the following output.
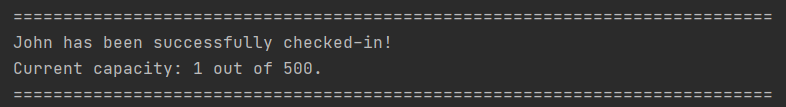
However, you should expect the following output when the maximum capacity is reached.

3.3 Listing all persons: listall
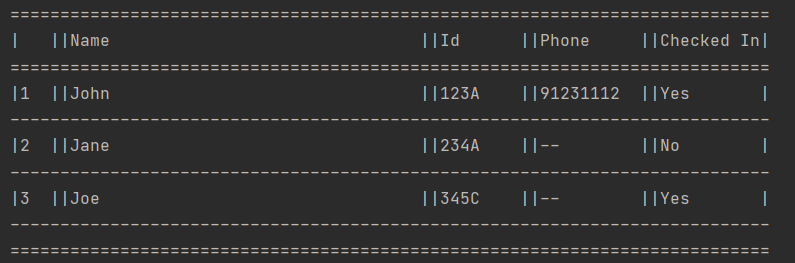
Supposed you want to find out all the visitors that had entered the venue,
it can be done with listall. This command shows a list of all persons
who have checked-in and checked out. The ID and phone numbers are also
shown in case you need to contact any of these visitors. However,
if the visitor’s phone number has not been registered with CYC, it will
be shown as --.
Format: listall
Example Input: listall
Example Output:
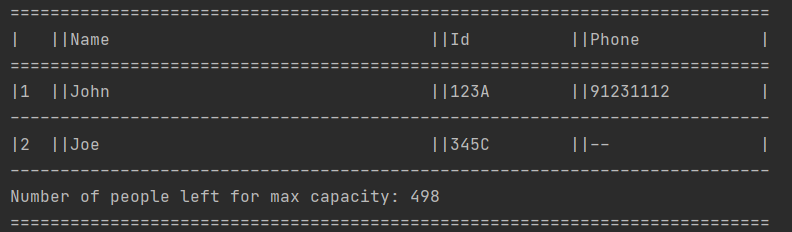
3.4 Listing checked-in persons only: listcheckedin
listcheckedin command is similar to listall, the only difference is that listcheckedin only
returns the list of visitors that are still in the venue or have not check out.
Shows a list of all persons with their details currently checked in. It also shows the number of people
remaining to reach the maximum capacity for that venue.
Format: listcheckedin
Example Input: listcheckedin
Example Output:
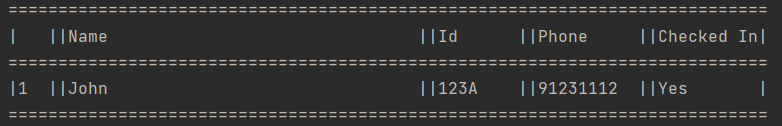
3.5 Finding a person by ID number: find
You can use find command if you need to check whether a particular visitor
is still in the venue or check for his/her particulars.
Given the person’s last 4 characters of ID, we can find the details of the person and status (Checked in, or checked out)
Format: find i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID
- First 3 characters of
LAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDshould be integers. Last character ofLAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDmust be an English alphabet letter.
Example input: find i/123A
Example Output:
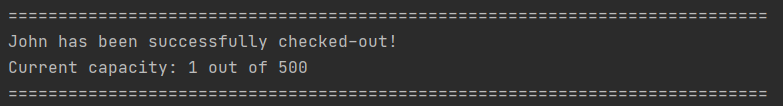
3.6 Check out a person: checkout
You can check out a visitor from CYC, when he/she is leaving from the venue via
checkout command. By doing so, you will be removing the visitor from checked in
list in CYC. However, person’s particulars will be retained for a faster
check in the following visit.
Format: checkout i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID
- First 3 characters of
LAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDshould be integers. Last character ofLAST_4_CHARS_OF_IDmust be an English alphabet letter. checkoutonly accepts 1i/flag, with the last 4 characters of ID.
Example input: checkout i/123A
Example output:
3.7 Clearing all entries: clear
clear command clears all entries stored by the program. It could be useful
to clear CYC data at the end of the day, or when required. However, this is
not recommended as you will lose track of the visitors who have not check out.
Therefore, use clear command with caution.
Format: clear
Example Input: clear
Example Output:

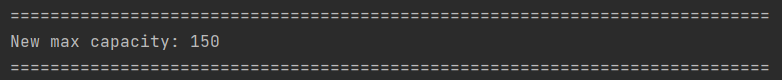
3.8 Edit venue capacity: editmax
In the event that requires the venue capacity to change, you
can update the new venue capacity in CYC using editmax command.
Edits the max capacity of the venue.
Format: editmax NEW_CAPACITY
NEW_CAPACITYmust be a positive integer and not more than six digits.- The program crashes if you do not provide
NEW_CAPACITY.- This bug will be fixed in the next release.
Example Input: editmax 150
Example Output:
3.9 Change storage location: movestorage
This command allows you to move the location of the saved file, if you desire a different location from the default setting. A suggested use would be to use it to backup files.
Additional Notes:
- The path specified has to be unused.
- The path specified will have
.txtto the end of it.- The previous location will be deleted by the program.
Format: movestorage NEW_DESTINATION
Example Input: movestorage /new/test
Example Output:

3.10 Exiting CYC: exit
exit command will save the current state of CYC before exiting the programme.
Format: exit
Example Input: exit
Example Output:
3.11 Visitor Log
CYC automatically saves the details of previous persons therefore providing the users with a convenient location to retrieve all particulars and details of visitors.
With Visitor log,
a person who have checked in before, does not have to input all his details
again when using the checkin command.
The person details are stored in /LogFile.txt in the same folder as the program.
You can reset Visitor Log by exiting CYC and deleting it before reboot.
3.12 Auto Save
The program automatically saves data to a .txt file after each command you input.
The program defaults to saving to /TrackingList.txt in the same folder as the program.
As such, you do not have to worry about saving the data or memory loss in case of
programme crash.
3.13 Changing save location
To change the save location, you can use the command movestorage. The command format for move storage
is stated above.
If the user deletes the folder of the new path, the program may run into write errors.
To resolve the issue, settings.properties should be deleted to reset the program state.
3.14 History
CYC automatically keeps a back up of the checkin and checkout history in history.txt file after
each check in and check out operation.
Users, such as event organiser or mall owners, could therefore study these data for future planning and necessary upgrade of facilities. History data is also stored in CSV format, comma separated values such that it can be extracted and cleaned to use for automatic data analytics.
Saving history
The program automatically saves the history to ‘history.txt’ file after each checkin and checkout operation.
Clearing history
In the unlikely event that, your machine runs out of storage space or you want to reset the history. You can follow these steps, to clear history.
To clear history, please follow the following steps:
- Exit CYC.
- Locate the directory of CYC on the computer.
- Locate
/History.txtand delete the file directly. (CYC will create a new History file upon a restart.)
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Please follow these steps:
- Follow the Quick Start guide and install CYC on the computer
- Transfer the
/History.txt,/LogFile.txtand/TrackingList.txtto the target computer’s main CYC folder. - Start CYC and it will automatically load the data.
Q: What does Clear command clears exactly?
A: Clear command only clears the visitors that are checked in. However, it does not clear the person log. Which
means if you had checked in a person with name: John, Id: 123A. After executing clear command, CYC will not allow you
to check in another person with name: James, Id: 123A as CYC will detect that the Id is a duplicate despite its two
different people.
5. Command Summary
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Help | help |
help |
| Check-in a person | checkin i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID n/NAME [p/PHONE_NUMBER] |
checkin i/123A n/John p/91231112 |
| List all person | listall |
listall |
| List checked-in persons only | listcheckedin |
listcheckedin |
| Find person by ID | find i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID |
find i/123A |
| Checkout a person | checkout i/LAST_4_CHARS_OF_ID |
checkout i/123A |
| Clear all entries | clear |
clear |
| Edit venue capacity | editmax NEW_CAPACITY |
editmax 100 |
| Move storage | movestorage PATH |
movestorage data/storage |
| Exit | exit |
exit |